- The platform, developed as part of the European GreenMED project, will help administrations, shipping companies, ports and energy operators plan their decarbonisation based on real data
- The observatory will promote the energy transition by gathering, harmonising and analysing key data on maritime traffic, energy consumption, emissions and bunkering infrastructure in the region
Valencia, 12 December 2025.- Last month, Athens hosted the closing meeting of the European energy transition project GreenMED, which aims to promote green maritime transport in the Mediterranean basin by analysing the energy demand of the current fleet and evaluating transition scenarios towards a sustainable future.
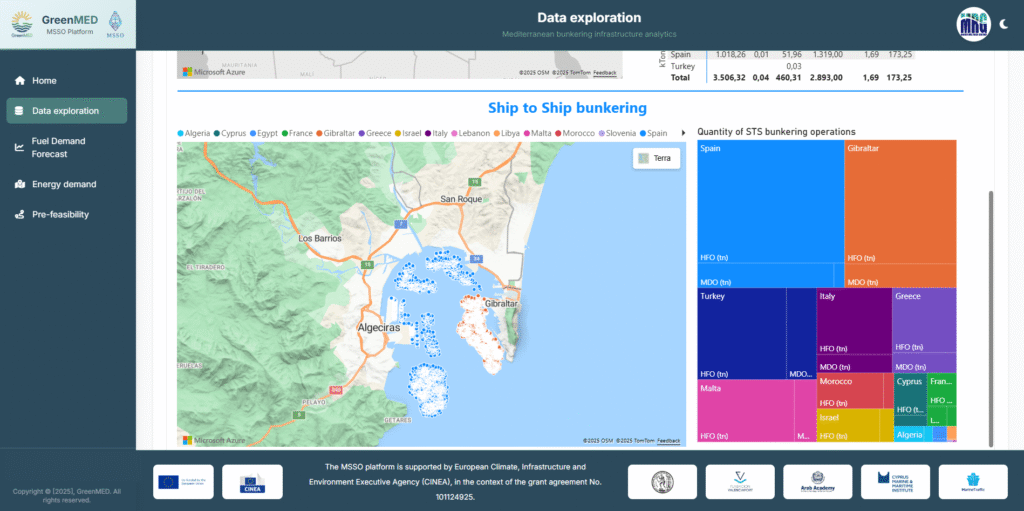
One of the main results of the project has been the launch of the Mediterranean Sustainable Shipping Observatory (MSSO), a digital platform that centralises and analyses key information on maritime traffic, energy consumption, emissions and bunkering infrastructure.
This observatory offers, for the first time, an integrated and accessible overview that will enable administrations, shipping companies, ports and energy operators to plan their decarbonisation based on solid and real data.
Fundación Valenciaport has played a key role in obtaining concrete and high-value results for the port sector, leading the analysis of technical, environmental and economic data.
In order to facilitate the interpretation of the information generated by the MSSO, the Foundation has developed a visual and intuitive tool that allows users to consult data on current bunkering supply (fuel availability and current market analysis) as well as a tool to consider scenarios for the evolution of supply in the region, taking into account the main technical and economic variables that will affect the evolution of demand.
This functionality will make it possible to identify trends, gaps and opportunities for the development of new bunkering or ship fuel supply infrastructure. Likewise, the viability of various alternative fuels, including methanol, ammonia, hydrogen and LNG, has been analysed according to the different types of ships and routes in the Mediterranean, providing a strategic basis for port energy planning and the deployment of new sustainable bunkering infrastructure.
Finally, a dynamic tool has been created that allows different alternative fuel supply scenarios to be simulated. Using parameters such as future prices and regulatory incentives, this tool will enable the economic viability of bunkering facilities to be estimated and different alternatives to be compared.
This solution is currently available free of charge on the GreenMED platform: https://msso.blue/.
The GreenMED Consortium
The initiative, coordinated by the National Technical University of Athens (NTUA), has had a budget of around €1 million, co-financed by the European Maritime, Fisheries and Aquaculture Fund (EMFAF) programme of the European Climate, Infrastructure and Environment Executive Agency (CINEA).
In addition to NTUA and the Valenciaport Foundation, three other entities are participating in the project: Cyprus Marine and Maritime Institute (CMMI), Marintrafik Opereisons Anonymi Etaireia Pliroforikis (MT) and the Arab Academy for Science, Technology & Maritime Transport.







